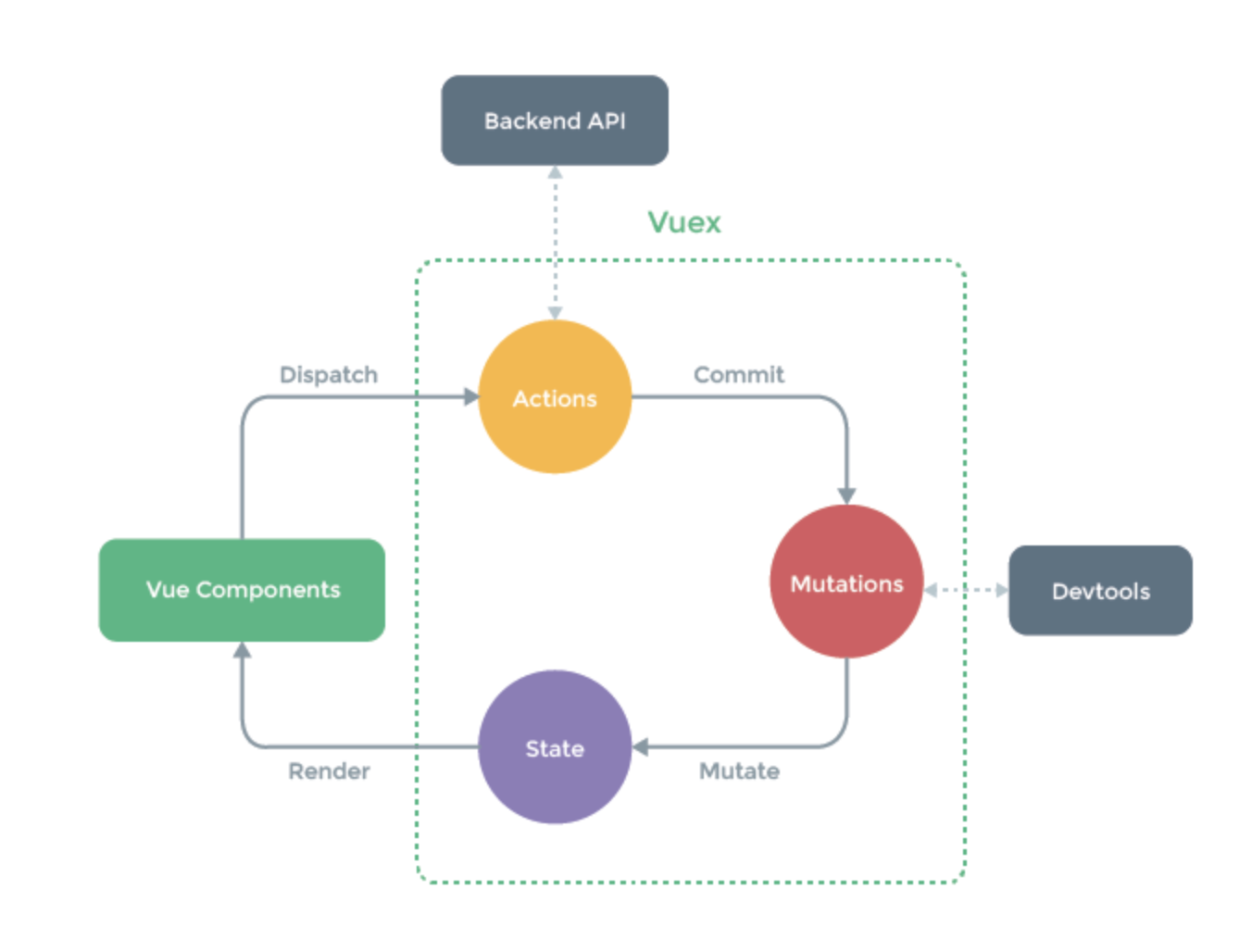
vuex原理
- state:单一状态树,类似于全局的一个容器
- getter:相对于state的计算属性
- mutations:定义同步方法
- actions:定义异步逻辑,请求过后再去调用mutations里的方法
ModuleCollection.js
export default class ModuleCollection{
constructor(options) {
this.register([], options);
}
register(path, rootModule) {
let rawModule = {
_raw: rootModule,
_children: {},
state: rootModule.state
}
if (!this.root) {
this.root = rawModule;
} else {
let parentNode = path.slice(0,-1).reduce((root, current) => {
return root._children[current];
}, this.root);
parentNode._children[path[path.length - 1]] = rawModule;
}
if (rootModule.modules) {
Object.keys(rootModule.modules).forEach(moduleName => {
this.register(path.concat(moduleName), rootModule.modules[moduleName]);
});
}
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
msg: 10
},
getters: {
add(state) {
return state.msg + 20;
}
},
mutations: {
syncAddTen(state, payload) {
console.log('最外层');
state.msg += payload;
}
},
actions: {
asyncAddTen({ commit }, payload) {
commit('syncAddTen', payload);
}
},
modules: {
a: {
state: {
msg_a: 10
},
mutations: {
syncAddTen() {
console.log('hello a');
}
}
},
b: {
modules: {
c: {
state: {
x: 12
},
mutations: {
syncAddTen() {
console.log('hello c');
}
}
},
d: {
mutations: {
syncAddTen() {
console.log('hello d');
}
}
}
}
},
f: {
mutations: {
syncAddTen() {
console.log('hello f');
}
}
}
}
})
- 目的是根据以上的代码构建出以下一个对象
- 核心算法就是使用path数组推进路径,比如,将b格式化模块挂载到a格式化模块下面,path=[…..,‘a’,‘b’],使用数组reduce方法推进到a模块那一层,然后将b的格式化模块挂载到a格式化模块的_children属性下

initModule.js
export default function installModule(Vue, store, rootState, path, rawModule) {
if (path.length > 0) {
let parentState = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((root, current) => {
return rootState[current];
}, rootState);
Vue.set(parentState, path[path.length - 1], rawModule.state ? rawModule.state : {});
}
let getters = rawModule._raw.getters;
if (getters) {
Object.keys(getters).forEach(getterName => {
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, getterName, {
get() {
return getters[getterName](rawModule.state);
}
});
});
}
let mutations = rawModule._raw.mutations;
if (mutations) {
Object.keys(mutations).forEach(mutationName => {
store.mutations[mutationName] = store.mutations[mutationName] ?
store.mutations[mutationName] : [];
store.mutations[mutationName].push(payload => {
mutations[mutationName](rootState, payload);
});
});
}
let actions = rawModule._raw.actions;
if (actions) {
Object.keys(actions).forEach(actionName => {
store.actions[actionName] = store.actions[actionName] ?
store.actions[actionName] : [];
store.actions[actionName].push(payload => {
actions[actionName](store, payload);
});
});
}
if (rawModule._children) {
Object.keys(rawModule._children).forEach(moduleName => {
installModule(Vue, store, rootState, path.concat(moduleName), rawModule._children[moduleName]);
});
}
}
- 这个函数的主要作用就是将子孙模块的state、getters、mutations、actions全部挂载到它们的根节点上
- 算法思想:递归,对于state还是使用path拼接
index.js
import ModuleCollection from './MuduleCollection';
import installModule from './initModule';
let Vue;
class Store{
constructor(options) {
this.vm = new Vue({
data: {
state: options.state
}
});
// this.getters = {};
// this.mutations = {};
// this.actions = {};
this.modules = new ModuleCollection(options);
installModule(Vue, this, this.state, [], this.modules.root);
}
commit = (mutationName, payload) => {
this.mutations[mutationName].forEach(fn => {
fn(payload);
});
}
dispatch = (actionName, payload) => {
this.actions[actionName].forEach(fn => {
fn(payload);
});
}
get state() {
return this.vm.state;
}
// register(moduleName, module) {
// if (!Array.isArray(moduleName)) {
// moduleName = [moduleName];
// }
// this.modules.register(moduleName, module);
// installModule(Vue, this, this.state, [], this.modules.root);
// }
}
const install = (_vue) => {
Vue = _vue;
/**
* 每次new一个vue实例时,都会去设置它的$store属性
*/
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
//根实例
if (this.$options.store) {
this.$store = this.$options.store;
//子组件
} else {
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.$store;
}
}
});
}
export default {
Store,
install
}
- 当外部使用Vue.use的时候,会默认去调用插件的install方法,以上的install方法里面使用传入的全局Vue向之后所有通过new运算符创建的vue实例,挂载上了$store
- 全局混入api可以查看官方文档 全局混入

