继承
原型链
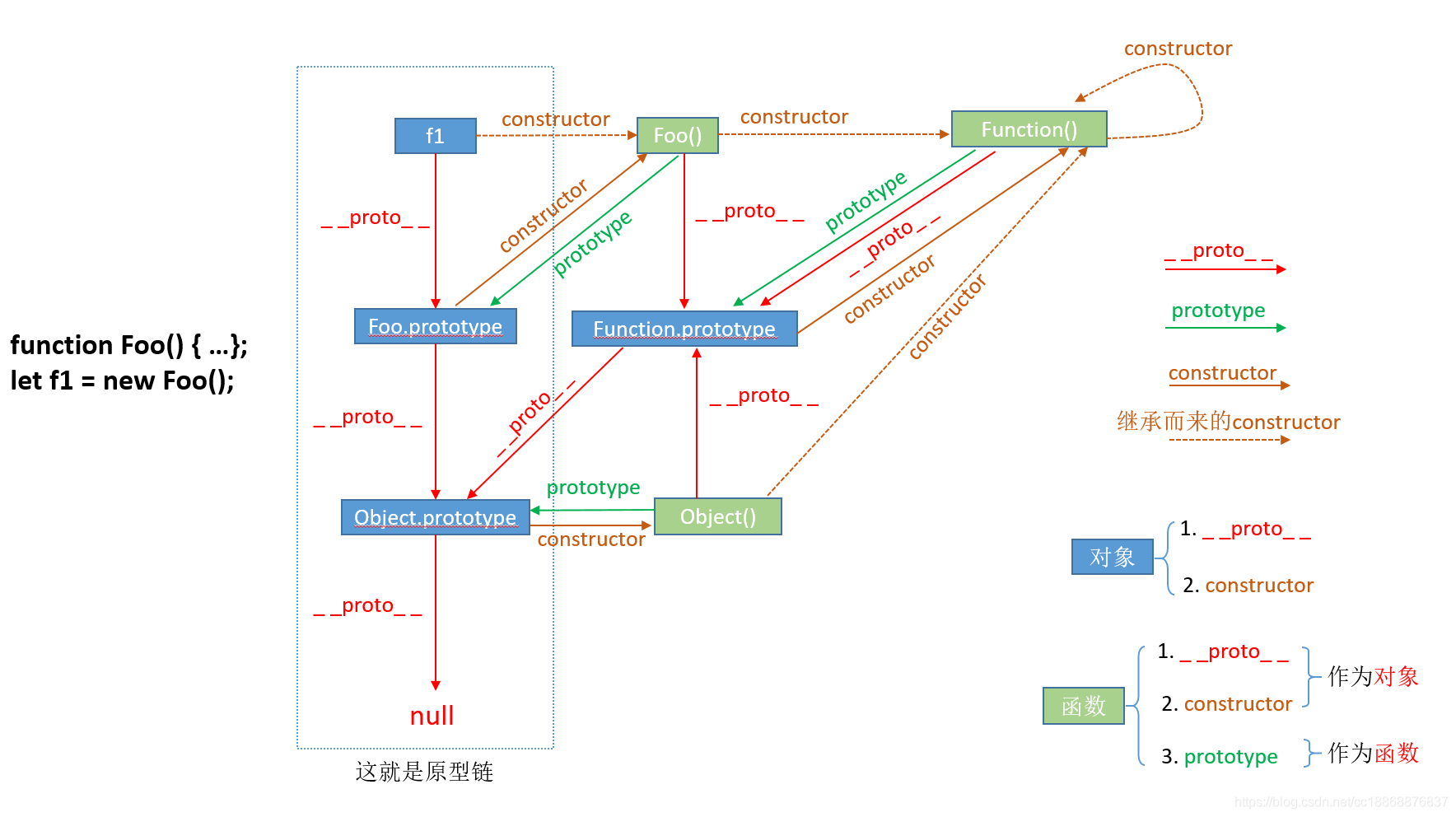
类式继承
-
类式继承是通过子类的原型prototype对父类实例化来实现的
-
具体步骤
- 创建子类和父类
- 子类的prototype属性指向父类的实例对象
- 缺点
- 如果父类中定义了实例属性,并且是个引用类型,那么子类的实例对其进行更改会相互影响()看以下案例
- 子类无法向父类传递参数
function Animal() {
this.color = ['red', 'green']
}
function Person() { }
Person.prototype = new Animal();
const per1 = new Person();//[ 'red', 'green' ]
const per2 = new Person();//[ 'red', 'green', 'blue' ]
console.log(per2.color);
per1.color.push('blue');
console.log(per2.color);
构造函数继承
-
构造函数继承是通过在子类的构造函数作用环境中执行一次父类的构造函数来实现的
-
具体步骤
- 在创建子类的同时,实现继承
- 缺点
- 不能调用父类原型上的方法
- 子类继承的属性或者方法,没有实现通用的共享
- 子类不是父类的实例
function Animal() {
this.color = ['red', 'green']
}
function Person() { }
Person.prototype = new Animal();
const per1 = new Person();
const per2 = new Person();
console.log(per2.color);//[ 'red' ]
per1.color.push('blue');
console.log(per2.color);//[ 'red' ]
组合继承
-
组合继承整合了类式继承和构造函数继承
-
优点
- 子类的实例中更改父类继承下来的引用类型不会相互影响
- 缺点
- 执行了两遍父类的构造函数
- 子类不是父类的实例
function Aniaml(age) {
this.age = age;
this.color = ['red'];
}
Aniaml.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log('hello world');
}
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
Animal.call(this, age);
}
Person.prototype = new Animal();
Person.prototype.getInfo = function () {
console.log(`${this.name} - ${this.age}`);
}
原型式继承
- 原型式继承本质上就是对类式继承的封装
- 与类式继承类似,继承的引用类型值会相互影响
function inheritObject(o) {
function F() { }
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
let obj = {
color: ['red']
};
const obj1 = inheritObject(obj);
const obj2 = inheritObject(obj);
console.log(obj2.color);//[ 'red' ]
obj1.color.push('blue');
console.log(obj2.color);//[ 'red', 'blue' ]
寄生式继承
-
寄生式继承本质上是对类式继承的二次封装
-
优点
- 相对于原型式继承,寄生式继承可以对继承的对象进行扩展
function inheritObject(o) {
function F() { }
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
function createObj(obj) {
let o = inheritObject(obj);
o.say = function () {
console.log('hello');
}
return o;
}
寄生式组合继承
- 寄生式组合继承是整合了寄生式继承和组合继承的一种理想的继承方式
- 它与组合继承的区别就是将子类的prototype指向了父类的prototype
function Animal(age) {
this.age = age;
this.color = ['red'];
}
Animal.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log('hello world');
}
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
Animal.call(this, age);
}
function inheritObject(subClass, faClass) {
const p = Object.create(faClass.prototype);
p.contructor = subClass;
subClass.prototype = p;
}
inheritObject(Person, Animal);
Person.prototype.say = function () {
console.log(`${this.name} - ${this.age}`);
}
const per1 = new Person('wqt', 21);
const per2 = new Person('ljt', 21);
console.log(per2.color);
per1.color.push('blue');
console.log(per2.color);
per1.sayHello();